Introduction to Chainlink and Chainlink Staking

stakefish recently joined the Chainlink blockchain as a validator. The aim of this article is to cover the Chainlink blockchain basics for new users by providing a brief overview of its history, tokenomics, and its availability of public staking.
What is Chainlink?
Chainlink started in 2017 and is a blockchain abstraction layer enabling universally connected smart contracts. Using a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink allows blockchains to interact securely with events, payment methods, and external data feeds providing the off-chain information that smart contracts need.
As one of the first networks to allow the integration of off-chain data to smart contracts, Chainlink aims to be the foundational infrastructure for the smart contract economy and the industry standard for oracle networks. Chainlink has enabled over $6.4 trillion in transactional value across Ethereum, Polygon, Solana, and 12 other blockchain networks.
Chainlink is a decentralized network of nodes that provide data and information from off-blockchain sources to on-blockchain smart contracts via oracles. Users can become node operators and earn revenue by running data infrastructure to help ensure the blockchain’s success. This process, along with extra secure hardware, eliminates the reliability issues that might occur if using only a single centralized source.
What is Chainlink Staking and how does it work?
The introduction of a new era of growth and security via Chainlink Economics 2.0 begins with staking.
Staking is a key mechanism that aims to bring a new layer of crypto-economic security to Chainlink. The value of oracle networks secured by Chainlink is growing day by day and with this growth, there is a need for increased crypto-economic security that maximizes the cost of an attack by malicious actors.
Currently, node operators are decentralized and perform well enough that further improvements only provide marginal gains. Chainlink staking will drive more significant security improvements via new incentives for the node operators and token holders.
The primary objective of Chainlink is to increase the security behind the infrastructure that supports Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi.
Chainlink Staking is being designed with four long-term goals in mind:

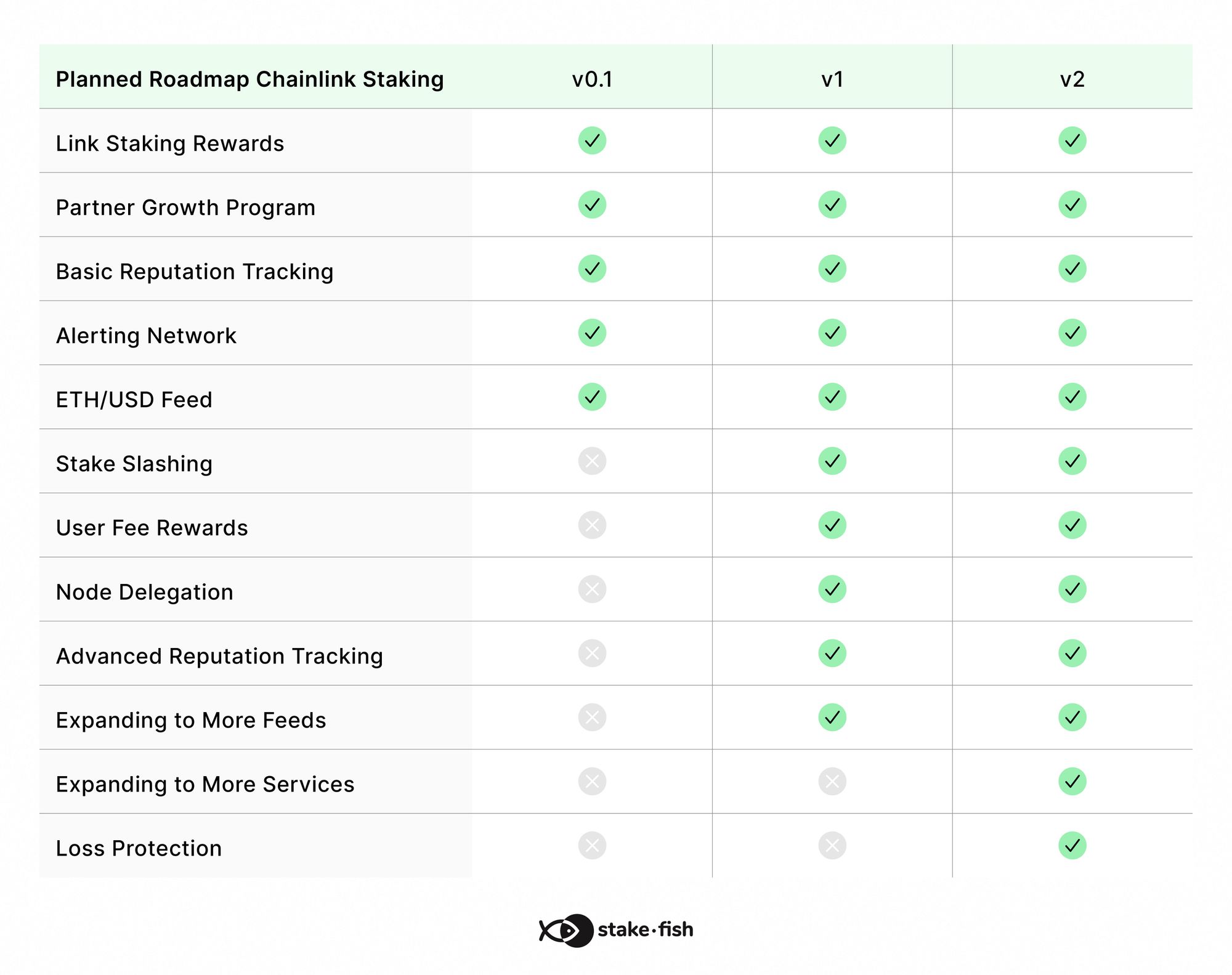
The implementation of LINK staking is being done gradually over time.
In the first phase, the focus will be on building a framework for reputation management, as well as the staking alerting system. In the second phase, slashing will be implemented to further boost security and user fees as rewards. Loss protection will arrive later in version two to help protect participants when an oracle network deviates from its service-level agreement.
The below roadmap reflects an overview of the planned approach to rolling out some of the key functionalities of Chainlink staking across multiple versions.
Where can I stake Chainlink?
Stake your LINK with stakefish using stake.link’s easy to use, secure liquid staking protocol, and earn staking rewards.
To learn more about Chainlink staking v0.1, we recommend reading What is Chainlink Staking? and Chainlink Staking: Exploring the Long-Term Goals, Roadmap, and Initial Implementation on the Chainlink website.
About stakefish
stakefish is the leading validator for Proof of Stake blockchains. With support for 20+ networks, our mission is to secure and contribute to this exciting new ecosystem while enabling our users to stake confidently.
Visit our website 🐠 | Telegram | Twitter | Instagram | YouTube | LinkedIn | Reddit





